Value Added and Non-Value Added Activities in Lean
This article on Value Added Non-Value Added Activities in Lean shall be a good read on how to differentiate between VA and NVA Activities.
This article on Value Added and Non-Value Added Activities in Lean shall be a good read on how to differentiate between VA and NVA Activities.
Value Added Non-Value Added Activities in Lean is a good start point for any Lean Improvement initiative
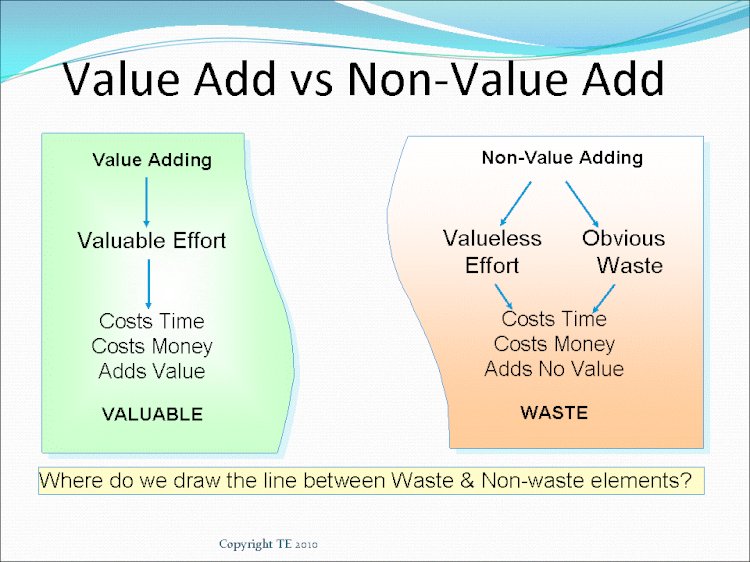
Lean is one of the most dynamic methodologies that aim at always looking at improvements in all business processes. Value Added and Non-Value Added Activities in Lean are ways to identify waste and taking steps to eliminate them. Waste in lean is considered to be like poison which has to be eliminated at all costs. Business activities in Lean are divided into two broad categories – Value Added and Non-Value Added.
Value Added activities: These activities are those which adds value to a business process or product and for which customer is willing to pay. Value Added activities help in converting a product from a state of raw material to a finished product in the least possible time, at minimum costs. It aims at completing a business activity correctly the very first time, and helping the business to deliver the product or service while fully conforming to customer requirements or specifications.
Non-Value Added activities: These are those which do not add any value to the product or service but are an inherent part of the process. Customers are not willing to pay for such services. These activities prove to be a burden on the organization and affect its efficiency. Valuable resources in the organization are engaged in completing these activities despite the fact that such activity is slowing the progress of the organization.
There are several examples of Non-Value Added activities found commonly among different organizations. Some of the most commonly found are:
• Process steps which are not needed
• Unnecessary movement of goods or resources within or outside the organization
• Unnecessary paper work within or in between departments which is not required
• Rework due to defects found in products
• Corrections or rechecking done due to important process steps not completed properly
• Services to customers(inside and outside) not properly delivered leading to customer dissatisfaction
• Unnecessary storage of raw materials or finished goods or storing more than required
• Important Organization resources such as expensive machinery or labor lying idle or waiting for work as inputs not delivered on time
• Delay in delivery to customers (inside and outside) due to unnecessary waiting time
Non-Value Added activities cause customer dissatisfaction by late delivery of goods and services which affect the credibility of the company as it is not able to deliver as per the committed/planned schedule. Also, the cost of such products and services is much more which ultimately customer is paying for. In such a scenario, customers will only stay with the company till the time they are able to find a suitable alternative.
Companies having Non-Value Added activities may survive in monopolistic conditions but such companies are rare to find in today’s world where efficiency and profitability are the benchmarks. Similarly, companies where efficiency and excellence is given foremost importance survive through all highs and lows of business cycles and continue to prosper long after their competitors have bitten dust.

 Pankaj Kumar
Pankaj Kumar 






























Comments (0)
Facebook Comments