Various Steps in FMEA
Various Steps FMEA. Business is often affected by problems, issues and defects which lead to loss in both financial terms and credibility.

Various Steps FMEA. Business is often affected by problems, issues and defects which lead to loss in both financial terms and credibility.
Various Steps in FMEA
Business is often affected by problems, issues and defects which lead to loss in both financial terms and credibility for the business organizations. Hence, companies analyze the potential risks that may affect it in future to safeguard itself from the likely negative consequences. FMEA is an excellent tool which helps the companies develops an effective defect prevention strategy.
Various Steps in FMEA
1. Process selection
2. Team selection
3. Process description
4. Identifying potential failures
5. Prioritization of problems
6. Designing solutions
7. Implementing solutions
8. Measuring impact of solutions.
1. Process Selection: First of all, a process has to be selected for the exercise. The selection can be made on the basis of various criteria such as importance of the process to the organization, process generating many defects, customer complaints, etc. The selection is usually made by the top management. FMEA is generally done as a part of improvement projects in many organizations.
2. Team selection: A leader is appointed by the top management. The leader then finalizes a cross-functional team of all the stakeholders involved in the process or expertise and gets it approved. The inputs of those persons or departments are also invited who are not part of the team but their work is likely to be affected.
3. Process description: A brief description of the process is done, generally with the help of a flowchart. The description can be an overview of few major steps or a detailed description having all the steps and sub-steps – the intention is to have an understanding of the process.
4. Identifying potential failures: Here, all the potential failure modes of each step of the process are identified. The presence of all the stakeholders is justified as each step is thoroughly analyzed and debated and its potential failure modes are documented.
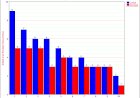
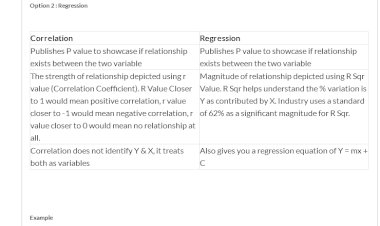
5. Prioritization of problems: Some of the failure modes that have been identified may frequently occur and some rarely occur. Hence, prioritization is done to solve those failure modes first which frequently occur. This is done by documenting the direct impact of the failure and how serious it is. This is decided by the team members purely on the basis of their experience and knowledge and is done in a mathematical manner.
6. Designing solutions: Once all the failure modes have been prioritized, then the team moves on to formulate solutions for them. The identified solutions may involve approvals from other stakeholders due to various factors such as process change, any extra investment/expenditure is required, resistance to implementation, etc.
7. Implementing solutions: After solutions are finalized and all necessary approvals are taken, the finalized solutions are implemented. The implementation may be done in a limited part of the process like a pilot project if large scale changes are involved.
8. Measuring impact of solutions: After a fixed period of time as decided, data is collected for the implemented solutions to analyze whether the identified failures have been eliminated or not. Once it is known that the failures have been successfully dealt with, then a Control Plan is prepared to sustain the improvements in the process.

 Pankaj Kumar
Pankaj Kumar 






























Anushtha
FMEA is a seven-step procedure. The steps include: 1. Planning and Preparing - In this step, we analyze the 5Ts of the analysis which are InTent (Why), Timing (When), Team (Who), Task (What), Tools (How). 2. Structural Analysis - In this step, a structured analysis is performed by clarifying the product in a detailed manner for the technical teams to analyze it. 3. Functional Analysis - In this step, the functions and the steps are analyzed properly on the basis of how the product is supposed to function. 4. Failure Analysis - In this step, the potential failures, their effects, and their causes are identified. 5. Risk Analysis - The severity, occurrence, and detection levels for failures are identified in this step. They are ranked on scales from 1 to 10. 6. Optimization - During this step, an action plan is prepared by the teams in order to mitigate the risks through prevention and detection. 7. Documentation - The final step is about recording all the results in the form of a document. This document includes a summary of the scope, details on high-risk failures, the required actions taken and their effectiveness, and plans for the present and future processes. Feel free to contact our experts at Visure Solutions in case you require any assistance on FMEA.