ISO 13053
ISO 13053 divides Six Sigma in to 5 different phases,which are typically known as an acronym of DMAIC. It is universally applicable to all business.

ISO 13053 divides Six Sigma in to 5 different phases,which are typically known as an acronym of DMAIC. It is universally applicable to all business.
ISO 13053
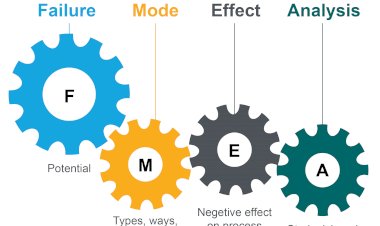
ISO 13053 standard has been specifically written by ISO to provide a framework for using Six Sigma as an improvement methodology for improving business processes in organizations. It typically divides Six Sigma into five different phases which are commonly known as DMAIC or Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control.
New Bitmap Image.
ISO 13053 provides basic guidelines or Best Practices for each of the individual stages of a Six Sigma project. It also describes how a Six Sigma project should be managed and the roles and skills needed for the personnel which are part of the project to complete their tasks properly. Finally, as it is common with other ISO standards, ISO 13053 is also universally applicable to all business organizations, whether they are manufacturing or service or have some other transaction related processes.
Six Sigma projects should be undertaken in organizations for achievement of its goals. But the primary pre-requisite is that the solution for the problem should not be known before the commencement of project. The various activities undertaken in a Six Sigma project can be broadly divided into following categories:
1) Identify problem – Various issues or problems affecting business processes should be identified and quantified regarding how much negative impact it is having on the business
2) Collect data for the problem – The data for the problem or issue affecting the business should be collected and verified for accuracy
3)Analyze data and get information – Detailed Analysis should be done on the data collected and verified to extract meaningful information relevant to the problem
4)Propose solution and implementation- Solution for the problem should be designed based on analysis and implemented
5)Verify if the goal has been achieved – Once the solutions have started taking effect, improved results should be analyzed to validate if the desired results have been achieved. Once it has been verified, then establishing controls to sustain this improvement.
Customer requirements and expectations should form the basis for each Six Sigma project. Customer requirements or “Voice of Customer” can be either for internal customer or external customer. It also defines the time line for Six Sigma projects in the organization. It is imperative that all activities undertaken in different phases are checked after each and every phase to ensure that the project is running as per the mandate received from the customer requirements.
For the purpose of validating whether the project has achieved its target or not, some sort of accounting framework should be established. This framework can be of financial in nature but customer expectation and safety also play an important part in this. This is to make sure that both the financial expectations and operational expectations from the project have been achieved. The performance for the project should be reviewed at fixed periods with the Project Sponsor to make sure that the project is on the right track.

 Pankaj Kumar
Pankaj Kumar 





























bcaa23
Well Explained Post. Its good to read the post which helps to know about ISO training and Certifications.