Structure of a Six Sigma project
Structure of a Six Sigma project
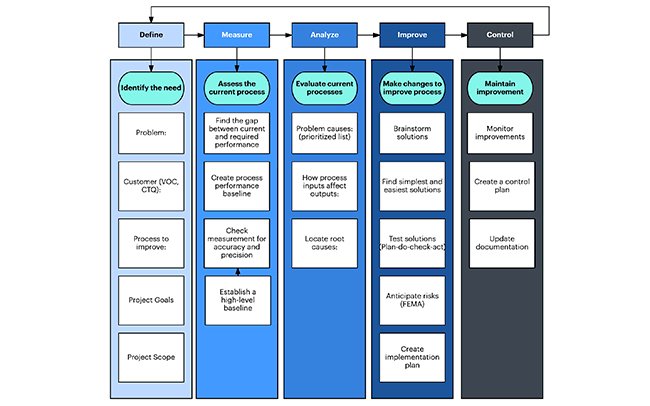
Structure of a Six Sigma project
Six Sigma has emerged as one of the most popular problem solving methodologies in today’s business environment. Business organizations throughout the world over are adopting Six Sigma and benefitting from it.
What should be the Structure of a Six Sigma project, Most of us know that Six Sigma has 5 steps of DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. But a typical Six Sigma project has many other steps where the problem or pain area in the business process is thoroughly studied and steps are formulated to get rid of these problems and pain areas. Apart from DMAIC, a Six Sigma project can be divided into following steps:
1. Understand the Problem: The problem occurring in the business process is mentioned and discussed among organizational hierarchy. Its impact is thoroughly studied and benefits calculated if the problem is solved. Considering all this, a target is decided and taken as a goal or objective to eliminate the pain area and solve the problem
2. Form the Team: As it is difficult to undertake a Six Sigma project alone, a team is formulated of different stakeholders or departments whose participation is required for the project. Roles and Responsibilities are assigned based on the expertise of the people and their importance emphasized in the completion of the project.
3. Understand the Process: Detailed process mapping is undertaken with all the steps mapped to get a thorough understanding of the process. This helps in the identification of the steps which are not needed and are present in the process but not documented
4. Gather Process Data: Data collection for the process is undertaken for further analysis to understand the magnitude of the problem
5. Analyze the process: The process is carefully analyzed and compared with the documented procedures to get a clear understanding and identify the gaps in the Process Design and the Process Performance
6. Identify possible corrective actions: Once the gap areas have been identified, various steps are taken such as Brainstorming with process experts to identify possible actions which can bring about improvements in the process
7. Screen/Experiment to select best action: Once all the possible actions have been written down, all the actions are carefully analyzed and final actions out of them are identified. This selection is made on the basis of possible benefits to business, cost required, ease of implementation, time duration, etc
8. Implement action: The final actions so identified are then implemented within a specific area, pre-decided time duration or pre-decided volume of work completed.
9. Verify action: After the pre-decided time duration or volume of work has been done, then again data is collected of the process to verify whether the benefits of the implemented steps have really been achieved or not
10. Sustain improvement: Once it has been verified that the intended improvements have been achieved, then a proper structure has to be established or the existing structure is fine-tuned to make sure that the improvements are here to stay and were not just fluke.

 Shishu Pal
Shishu Pal 




























Comments (0)
Facebook Comments