Requirements for a Good Control Plan
Requirements Good Control Plan. An ideal Control Plan should be made by a team comprising of all the key persons or departments involved in the process.
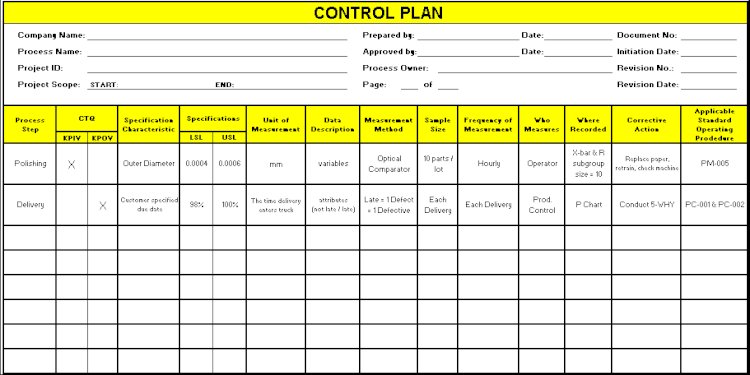
Requirements Good Control Plan. An ideal Control Plan should be made by a team comprising of all the key persons or departments involved in the process.
Requirements for a Good Control Plan
A well designed and formulated Control Plan can go a long way towards ensuring that the process remains within control and continues to fulfill customer requirements. But making a control plan requires answer to certain key questions:
• How a good control plan is prepared?
• Who prepares the control plan?
• Who looks over and implements the control plan?
• What are the inputs required for a good control plan?
What are the Requirements for a Good Control Plan
An organizational level Control Plan can be made by the top management where all the senior personnel give their inputs. But If the Control Plan is being made for a process, then it should be responsibility of either the Process Owner or he should play a key role in its formulation. This is because he knows all the nooks and corners of the process and has a clear idea of the scenario where process might fail. Also, the future implementation and regular updating of Control Plan is most likely expected to be his responsibility.
An ideal Control Plan should be made by a team comprising of all the key persons or departments involved in the process. Some important things which should be considered while creating a Control Plan are:
1. Measurements: For evaluating the performance of the process, some measurement criteria would have to be decided. The measurement can be of any numerical type like quality score, output, etc.
2. Specifications: The measurement would have to be based on limits which can be derived from the specifications provided either by the customer or by any law. Specifications can be provided by the organization itself also.
3. Inputs and outputs. The process would require certain things as inputs and will give results as certain output. This will require mentioning what inputs are required to get the desired output, in what quantity and what time duration is needed.
4. Major steps involved: The major steps or sub-processes involved which are vital to the functioning of a process should be mentioned along with their success criteria and steps to be taken in case any of the steps fail. Mistake proofing should be done wherever possible to minimize the occurrence of fail scenarios.
5. Frequency of monitoring and reporting: A fixed time period should be mentioned to monitor and report the performance of the process and major steps also of the process, if needed.
6. Sampling method: An appropriate sampling method as required by the process should be mentioned. Sampling methods can vary for different steps of the process.
7. Repository: A repository for storing information should be there for extracting information whenever needed. It will enable the process team to closely monitor the process performance and whenever any special cause occurs, data can be extracted for analysis to understand this special cause. This will also help in the generating reports about process performance at fixed time periods.
8. Fixing deviations: Remedial actions are taken for whatever deviations are found. This will help in preventing recurrence of these problems.
9. Process Owner, Stakeholders and Responsible: The names of the process owner, persons responsible for various steps of process, their monitoring and reporting and other key activities along with other stakeholders must be mentioned to identify which persons are involved in the process.

 Pankaj Kumar
Pankaj Kumar 





























Comments (0)
Facebook Comments