Six Sigma Project Prioritization
Six Sigma Project Prioritization
This article about Six Sigma Project Prioritization shall help the audience understand how to prioritize projects ideas and choose.
Six Sigma Project Prioritization
Master Black Belts or the PE Department will have to handle a challenge to choosing the project amongst the several options available.
Once there is a project ideation infrastructure as a critical next step shall be some analysis that could make a strong business case for project idea to be chosen amongst the various available options.
Prioritization could be managed upon carefully evaluating the CTQs important to driving the initiative direction. I personally feel that three critical elements must be evaluated:
1) Project alignment to organizational goals
Organizational Goals and Projects must have the same focus. Alignment to the organizational vision/mission/goals/strategies could be of key importance.
a) Customer success Customer Success shall always remain the key metric for any organization. NPS or customer success scores, improvement initiative on misses on some contractual obligation, attention to customer pain, lost business analysis, new product initiative etc. shall take precedence above most themes.
customer metric (already dealt with earlier) like OTR (order to remittance), ITO (Inquire to order), Sales Closure TAT, revenue, Margin etc. shall have to be built into the prioritization method for the sign off of the lean six sigma initiative.
Change management challenges
Change Management challenges must be evaluated prior to giving a go ahead. The complexity of change management will always be a key factor to project prioritization decision.
a) Stakeholder Participation
Availability of key stakeholder, MBB Participation etc. is a key change management need for any initiative. It is important that we measure the project success likelihood with participation from the relevant stakeholders.
b) Leadership Participation
c) Project Complexity – Complexity of the initiative could be looked at as a key metric for prioritization.
d) Competence availability
e) Infrastructure Availability
1) Statutory Norms
2) Knowledge Base
3) Technology Base
3) Project Success measurement
a. Risks associated: Associated risks of projects (keeping in mind the various input needs) could be a great way of looking at decision on project priority.
b. Capability availability- Capability needs could be a key decision criteria for project prioritization. One must consider that capability will be a key success criteria for project success.
c. Resource Availability:Resources needed for the success of the project is an important aspect to consider when looking at project prioritization. For an initiative when resources are not available in the organization or are costlier or scarce etc. we should prioritize basis resource availability.
d. Time index of return – One may want to measure time index of return for project prioritization. Time Index of return will be a beneficial index to consider in project prioritization.
**** Thoughts – Scope & Quality
**** Thoughts – Evaluate Project Management Knowledge Areas
4) ROI Index of the initiative
One must always understand that cost of improvement should never be too high and the benefit measurement must be proportional to the Cost needed. Hence not using cost as the decision criteria will be beneficial as low cost may not always mean that the project is a priority, nor is the case when cost is high it is always low priority. Hence usage of ROI could be a better index.
5) Replication option in other parts of the organization– Improvement Initiatives lot of times can be replicated in different part of the organization, and this can help in replicating the lessons’ learnt to other parts of the organization.
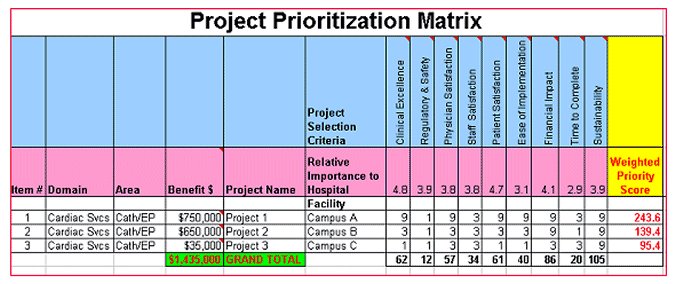
Example of a possible Prioritization Matrix to be used in an organization as used in ISO 13053:2011 Part 1
Project title (A) Customer importance (B) Expected total project cost (C) Likelihood of project success (D) Expected contribution to profit (E) Applicability to other areas (F) Project priority number (G) Project order
Invoice error investigation 8 2 9 5 4 2,880 2
Low yield on XXX line 6 5 7 8 8 13,440 1
Etc.
NOTE 1 The ranks are on a 1 to 10 scale with 1 being the worst and 10 the best.
NOTE 2 The value in column (F) is the product of the ranks in columns (A) to (E).
NOTE 3 The project order in column (G) is the ranking of the values in column (F).
Another Example for a Project Prioritization Grid.
Criteria Weightage
Strategic Criticality
(Importance of project in terms of Criticality to Business) 15%
Relation with organization’s Vision
(Relation between Organization’s Goal & Project initiated)
a) >80% – Optimising Business activities / Striving to achieve SLA / targets
b) 50% to 80% – Enhancement of operations
c) <50% – Other Baselining activities 15% Project Leadership (Project Champion/Monitored by) 15% Target Reduction (Percentage reduction of defect from existing level) 10% Cost Benefit of Project (Savings generated to Organizational by project) 10% Project Cost benefit sharing (Project profit will be shared by Organizational only or by Client too ) 5% Process Duration in Organizational (How old the process in Place) 5% Project outcome (Expected results of Project) 5% Project Type (>50% of weekly time is considered as Full time project, else part time) 5%
Period of Project
(Duration of project) 5%
Project Review Frequency
(What will be review frequency of the project) 10%

 Pankaj Kumar
Pankaj Kumar 





























Comments (0)
Facebook Comments